3D-BIOPRINTED TISSUES CAN BE STORED IN THE FREEZER UNTIL THE NEED!
The short shelf life of 3D tissues limits their clinical use. In the case of organ transplantation, the tissue produced by the bioprinting method must be transported quickly to the place where it is needed. Otherwise, the 3D-bioprinted tissue will lose its vitality.
Researchers have published a study combining 3D bioprinting and cryopreservation technique to create tissues that can be stored in a -196°C freezer and defrosted within minutes for use when needed.
Biomedical engineer Y. Shrike Zhang says that there is no shelf life in the traditional bioprinting method, 3D tissues are used after bioprinting. With the cryobioprinting method, you can bioprint as much as you want and store the products in a frozen state.
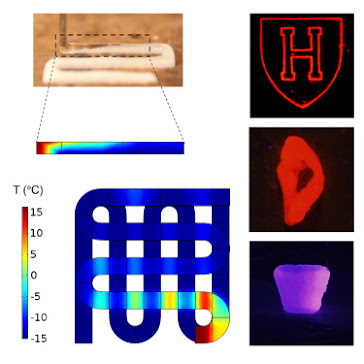
The bioink is flowed through the nozzle to create the defined shape, allowing the structure to form layer by layer. Bioink consists of a gelatin-like scaffold in which living cells are embedded. In cryobioprinting, the hydrogel is made on a cold plate maintained at -20 °C. After printing, the tissues are transported to cryogenic conditions for long-term storage.
Bioprinting at low temperatures allows complex shapes to be created. The bioink printed on the cold plate freezes in milliseconds and the structure does not lose its original shape. In this way, independent 3 dimensional structures that can withstand their own weight are formed.
For cells to survive at cryogenic temperatures, a cryopreservative agent must be used that prevents osmotic shock and limits the formation of ice crystals that can damage the cell membrane. Y. Shrike Zhang and his team also investigated the combination of cryopreservative agents that provide the highest cell viability.
It has been shown that tissues can last for at least 3 months before being brought back to life. Tissues produced by the bioprinting method will be able to be frozen for a long time, allowing greater collaboration among researchers to develop these applications.
3 BOYUTLU KRİYOBİYOBASKI YÖNTEMİ İLE ÜRETİLMİŞ DOKULAR İHTİYAÇ ANINA KADAR DONDURUCUDA SAKLANABİLECEK!
3 boyutlu dokuların kısa raf ömürleri, klinik kullanımını sınırlandırmaktadır. Organ nakli durumunda, biyobaskı yöntemiyle üretilmiş dokunun ihtiyaç duyulan yere hızlı bir şekilde nakledilmesi gerekmektedir. Aksi takdirde 3 boyutlu doku, canlılığını kaybedecektir.
Araştırmacılar -196 °C sıcaklığa sahip dondurucuda saklanabilen ve ihtiyaç anında kullanılmak üzere dakikalar içinde çözülebilen dokular oluşturmak için 3 boyutlu biyobaskı ile kriyoprezervatif tekniğini birleştiren bir çalışma yayınladı.
Biyomedikal mühendisi Y. Shrike Zhang , geleneksel biyobaskı yönteminde raf ömrünün olmadığını, 3B dokuların biyobaskıdan sonra kullanıldığını söylüyor. Kriyobiyobaskı yöntemi ile istediğiniz kadar biyobaskı yapabilir ve ürünleri donmuş durumda saklayabilirsiniz.
Belirlenmiş şekli oluşturmak için biyomürekkep nozuldan akıtılarak, yapının katman katman oluşması sağlanır. Biyomürekkep canlı hücrelerin gömülü olduğu jelatin benzeri yapı iskelesinden oluşmaktadır. Kriyobiyobaskıda ise, hidrojel -20 °C sıcaklıkta tutulan soğuk bir plakanın üzerine yapılır. Dokular yazdırıldıktan sonra uzn süreli saklama için kriyojenik koşullara taşınır.
Düşük sıcaklıklarda yapılan biyobaskı, karmaşık şekiller oluşturulmasına imkan sağlar. Soğuk plaka üzerine basılan biyomürekkep milisaniyeler içinde donar ve yapı orijinal şeklini kaybetmez. Bu sayede kendi ağırlığına dayanabilen bağımsız 3 boyutlu yapılar oluşur.
Hücrelerin kriyojenik sıcaklıklarda hayatta kalabilmesi için ozmotik şoku önleyen ve hücre zarına zarar verebilecek buz kristallerinin oluşumunu sınırlayan bir kriyoprezervatif ajan kullanılmalıdır. Y. Shrike Zhang ve ekibi, en yüksek hücre canlılığını sağlayan kriyoprezervatif ajanların kombinasyonunu da araştırmışlardır.
Dokuların hayata döndürülmeden önce en az 3 ay dayanabileceği gösterilmiştir. Biyobaskı yöntemiyle üretilen dokular, uzun süre dondurulabilecek ve araştırmacılar arasında bu uygulamaları geliştirmek için daha fazla işbirliğine olanak sağlayacaktır.
REFERENCES
3D-bioprinted tissues can now be stored in the freezer until needed
Comments
Post a Comment